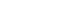Home»Anti-Oxidants
:: Oxidative Stress
» What is Oxidative Stress?
Oxidative Stress is the name given to the damage caused to cells by overly reactive oxygen-containing molecules. It is thought to play a role in many human diseases as oxidation reactions can produce damaging free radicals.
What are free radicals?
To best explain what free radicals are we must first return to some of our GCSE chemistry.
Our bodies are made up of many cells, which are made up of many molecules, which in turn are made of 2 or more atoms.
These atoms are made up of protons (positively charged) and neutrons within a nucleus, surrounded by electrons (negatively charged). The number of protons an atom has in a nucleus (the atomic number on the periodic table) determines how many electrons there will be surrounding, or orbiting the atom. The electrons are used in chemical reactions and are what bind atoms together to make molecules. The electrons orbit an atom in what are known as 'shells'. The first shell can contain 2 electrons. When this is full the electrons start to fill a second shell. This second shell becomes full at 8 electrons and so any further electrons begin to fill a third shell and so on and so forth. The number of electrons in the outer shell determine the chemical behaviour of an atom. |
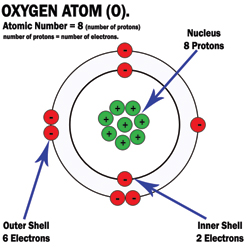 |
Atoms that have full outer shells are very stable and inert. All atoms are trying to reach this stable state. To do this, atoms with unpaired or single electrons on the outer shell (like the oxygen atom in the picture) will react with other nearby atoms in one of two ways:- 1. By stealing or donating electrons to empty or fill its outer shell. Normally the bonds that bind molecules together do not split in a way that would leave an unpaired electron. However when it does happen the molecule becomes a free radical. This free radical molecule will immediately look for another molecule to steal an outer shell electron from. When it does this the robbed molecule then becomes the free radical, and the process continues. |
 |
The result of this cascade of free radicals could be a damaged cell.
What are ORAC Units?
The ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) unit, ORAC value, or "ORAC score" is a method of measuring the anti-oxidative capacity of different foods and supplements. It was developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health. Foods that are higher on the ORAC scale will more effectively neutralize free radicals.
| Apple Cider Vinegar With Mother | Apple Cider Vinegar Benefits | Apple Cider Vinegar Candida |